
Guard dogs have been revered throughout history for their remarkable ability to protect homes and families. These loyal companions not only offer physical protection but also provide peace of mind. Understanding the best guard dog breeds and their characteristics is crucial for anyone considering adding a guard dog to their household.
What is a Guard Dog, and Why Are They Important?
A guard dog is a breed specifically trained to provide security and protect property. Unlike watchdogs, which alert owners to intruders, guard dogs are typically trained to act aggressively if a perceived threat approaches. The history of guard dogs dates back to ancient civilizations, where they were used to protect livestock, homes, and even kings and queens.
Difference Between Guard Dogs, Watchdogs, and Protection Dogs
- Guard Dogs: Trained to respond to threats with action. They are often used to protect property and people and can be aggressive towards intruders.
- Watchdogs: Alert owners to the presence of an intruder through barking or other signals. They do not necessarily act aggressively.
- Protection Dogs: Professionally trained to protect their owners from harm and often used by law enforcement or security personnel.
Why Choosing the Right Guard Dog Breed Matters
Selecting the right guard dog breed is essential for several reasons:
- Temperament: The breed’s temperament needs to align with your family’s needs. Some breeds are more aggressive, while others are more protective but gentle.
- Size: The size of the dog can affect how effective it is in guarding. Larger breeds might be more intimidating, while smaller breeds may be better suited for certain environments.
- Training: Different breeds have varying levels of trainability. A breed that is easier to train will likely be more effective as a guard dog.
Guard dogs can act as a deterrent to intruders and provide a sense of security for families. However, they require proper training and care to fulfill their role effectively.
What to Consider When Choosing the Best Guard Dog Breed

Choosing the best guard dog breed involves more than just picking the breed with the best reputation. Several factors need to be considered to ensure that the guard dog fits well into your family and lifestyle.
Family and Lifestyle Compatibility
1. Family Dynamics:
- Children: If you have young children, you’ll need a guard dog breed that is known to be patient and gentle with kids. Breeds like the German Shepherd and Boxer are often recommended due to their balanced temperament.
- Other Pets: Some guard dogs have a high prey drive and may not get along well with other animals. Breeds such as the Rottweiler and Doberman Pinscher might require careful introduction and supervision.
2. Living Environment:
- Apartment vs. House: Larger breeds like the Bullmastiff or Great Dane may not be suitable for apartment living due to their size and exercise needs. Smaller, more adaptable breeds might be better for confined spaces.
- Yard Space: If you have a large yard, breeds that require more exercise and space, such as the Belgian Malinois or Rhodesian Ridgeback, may thrive in that environment.
Training and Socialization Needs
1. Early Training and Socialization:
- Importance: Early training and socialization are crucial to ensure a guard dog develops into a well-behaved and effective protector. Exposure to various people, environments, and situations helps prevent aggression and promotes adaptability.
- Methods: Socialization can include puppy classes, exposure to different stimuli, and positive reinforcement techniques.
2. Training Methods:
- Professional Training: Hiring a professional trainer can be beneficial, especially for complex behaviors and obedience training. This is particularly useful for high-drive breeds like the Belgian Malinois.
- DIY Training: For those who prefer to train at home, consistency and positive reinforcement are key. Techniques should be tailored to the breed’s characteristics and needs.
Energy Levels and Exercise Requirements
1. Exercise Needs:
- High-Energy Breeds: Breeds like the Belgian Malinois and Rhodesian Ridgeback have high energy levels and require regular physical and mental stimulation. Daily exercise routines, including walks, playtime, and training sessions, are essential.
- Low-Energy Breeds: Some guard dogs, such as the Bullmastiff, have lower energy levels but still need regular exercise to maintain health and prevent behavioral issues.
2. Balancing Work and Exercise:
- Incorporate exercise into your daily routine to ensure your guard dog remains fit and healthy. Activities like agility training, obedience drills, and interactive toys can help meet their physical and mental needs.
Health and Lifespan Considerations
1. Common Health Issues:
- German Shepherds: Prone to hip dysplasia and certain genetic conditions. Regular vet check-ups and a healthy diet can help manage these risks.
- Rottweilers: May face issues like heart disease and joint problems. Monitoring their health and providing appropriate care is essential.
2. Lifespan:
- The lifespan of guard dogs varies by breed. For example, German Shepherds typically live around 9-13 years, while Bullmastiffs may have a shorter lifespan of around 8-10 years. Consider the long-term commitment required for each breed.
Top 10 Best Guard Dog Breeds

Selecting the best guard dog breed depends on various factors, including temperament, training needs, and compatibility with your lifestyle. Here are ten of the best guard dog breeds known for their protective instincts and effectiveness as guardians.
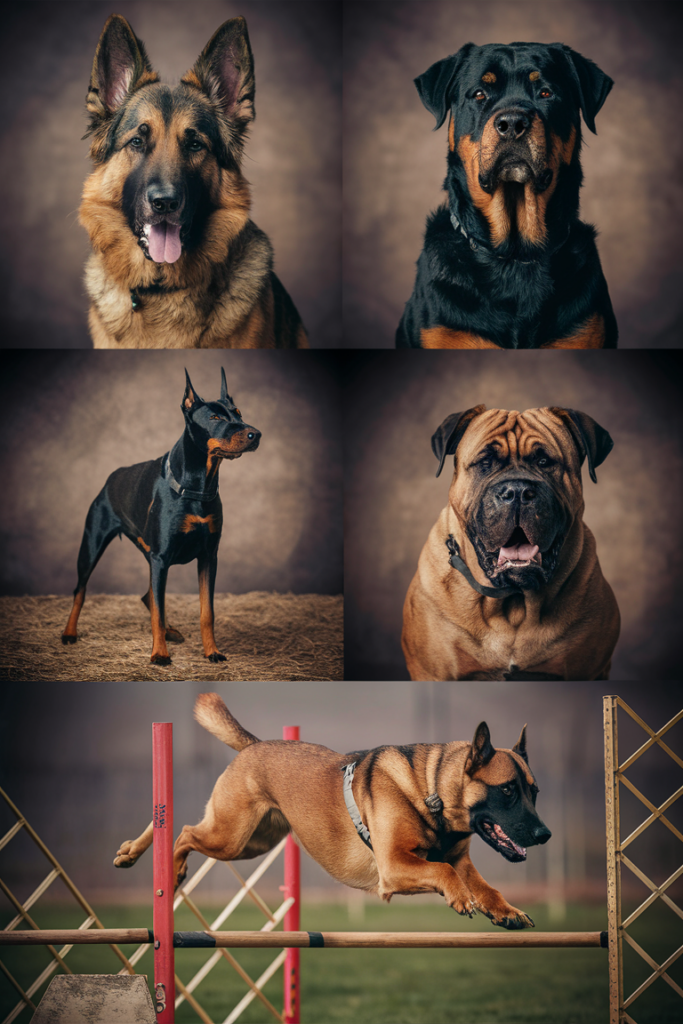
1. German Shepherd
Overview of the Breed: The German Shepherd is one of the most popular and versatile guard dogs, known for its intelligence, loyalty, and strong work ethic. Originally bred as a herding dog, the German Shepherd has proven to be an excellent protector and service dog.
Why German Shepherds Are Excellent Guard Dogs:
- Temperament: German Shepherds are highly alert, confident, and courageous. They are natural protectors and respond well to training.
- Training: They are highly trainable and excel in obedience and protection training. Their intelligence makes them quick learners.
Training Tips Specific to German Shepherds:
- Consistency: Be consistent with commands and rewards.
- Socialization: Early socialization with people and other animals is crucial to prevent aggression.
- Mental Stimulation: Engage them in activities that challenge their intellect, such as puzzle toys and advanced obedience training.
2. Rottweiler
Characteristics: The Rottweiler is a powerful and robust breed, known for its protective nature and loyalty. Historically used as a guard and herding dog, the Rottweiler remains a popular choice for security.
Why Rottweilers Are Effective Protectors:
- Strength: Their physical strength and imposing presence are effective deterrents for intruders.
- Loyalty: Rottweilers are deeply loyal to their families and can be very affectionate with proper training.
Key Training Tips for Rottweilers:
- Early Socialization: Introduce them to various environments and people from a young age.
- Firm Leadership: Establish clear boundaries and rules.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use positive reinforcement techniques to encourage good behavior.
3. Doberman Pinscher
Characteristics: The Doberman Pinscher is known for its sleek appearance, agility, and high energy levels. This breed combines speed and strength, making it an excellent choice for protection.
Why Dobermans Are Effective Guard Dogs:
- Agility: Their speed and agility make them effective in guarding and protection.
- Alertness: Dobermans are highly alert and responsive, often sensing threats before they become apparent.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Consistency in Training: Use consistent commands and reward systems.
- Socialization: Expose them to different people and situations to prevent fear-based aggression.
- Physical Exercise: Ensure they get plenty of exercise to keep them physically and mentally healthy.
4. Bullmastiff
Characteristics: The Bullmastiff is a large and powerful breed, originally developed to guard estates. Known for its gentle demeanor with family, the Bullmastiff is an excellent choice for a guard dog.
Why Bullmastiffs Are Effective Guardians:
- Size and Strength: Their sheer size and strength act as a deterrent to intruders.
- Protective Instincts: They are natural protectors and form strong bonds with their families.
Training Tips for Bullmastiffs:
- Early Training: Begin training early to manage their size and strength.
- Socialization: Ensure they are socialized with different people and situations.
- Exercise Needs: While not overly energetic, they still require regular exercise to stay healthy.
5. Belgian Malinois
Characteristics: The Belgian Malinois is a high-energy, intelligent breed often used in police and military roles. Its agility and trainability make it an excellent choice for security and protection.
Why Belgian Malinois Are Top Guard Dogs:
- High Intelligence: Their intelligence allows them to perform complex tasks and respond well to training.
- Agility and Speed: Their agility and speed make them effective in various protection scenarios.
Training and Care Tips:
- Intensive Training: Engage in rigorous training and provide mental stimulation.
- Socialization: Early and continuous socialization is essential.
- Exercise Requirements: They need ample physical and mental exercise to stay healthy and happy.
6. Boxer
Characteristics: The Boxer is a playful and energetic breed known for its loyalty and protective nature. While they are friendly and good with children, they are also effective as guard dogs.
Why Boxers Are Effective Guard Dogs:
- Playfulness: Their playful nature does not detract from their ability to guard and protect.
- Loyalty: Boxers are very loyal and protective of their families.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Consistent Training: Use consistent commands and reward-based training methods.
- Socialization: Introduce them to various people and environments to build confidence.
- Regular Exercise: Provide plenty of exercise to manage their energy levels.
7. Cane Corso
Characteristics: The Cane Corso is an Italian breed known for its strength and protective instincts. This breed is often used for guarding homes and property.
Why Cane Corsos Are Top Guard Dogs:
- Strength and Power: Their physical strength makes them formidable protectors.
- Loyalty: Cane Corsos are highly loyal and protective of their families.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Early Training: Start training early to manage their powerful presence.
- Socialization: Early socialization is crucial to prevent aggression.
- Exercise Needs: Regular exercise is essential to maintain their health and manage their energy.
8. Akita
Characteristics: The Akita is a large and powerful breed known for its loyalty and protective instincts. Originating from Japan, the Akita is a devoted family guardian.
Why Akitas Are Effective Guard Dogs:
- Protective Instincts: They are naturally protective and can be wary of strangers.
- Loyalty: Akitas are fiercely loyal to their families.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Early Socialization: Introduce them to different environments and people from a young age.
- Consistent Training: Use consistent commands and positive reinforcement.
- Exercise Requirements: Provide regular exercise to manage their energy and maintain their health.
9. Great Dane
Characteristics: The Great Dane is known for its imposing size and gentle nature. While they are gentle giants with families, their size and presence make them effective guard dogs.
Why Great Danes Are Effective Guardians:
- Size and Presence: Their large size acts as a deterrent to intruders.
- Gentle Nature: Despite their size, they are often gentle with families and children.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Early Training: Begin training early to manage their size and strength.
- Socialization: Expose them to different situations and people.
- Exercise Needs: Ensure they get regular exercise to stay healthy and maintain their size.
10. Rhodesian Ridgeback
Characteristics: The Rhodesian Ridgeback, originally bred to hunt lions in Africa, is known for its strength and independence. This breed is also an excellent guard dog.
Why Rhodesian Ridgebacks Are Effective Guard Dogs:
- Strength and Independence: Their strength and independence make them formidable protectors.
- Alertness: They are highly alert and responsive to their environment.
Training and Socialization Tips:
- Early Socialization: Introduce them to different people and environments.
- Consistent Training: Use positive reinforcement to encourage good behavior.
- Exercise Needs: Provide ample exercise to keep them fit and healthy.
Training Your Guard Dog: Tips and Techniques
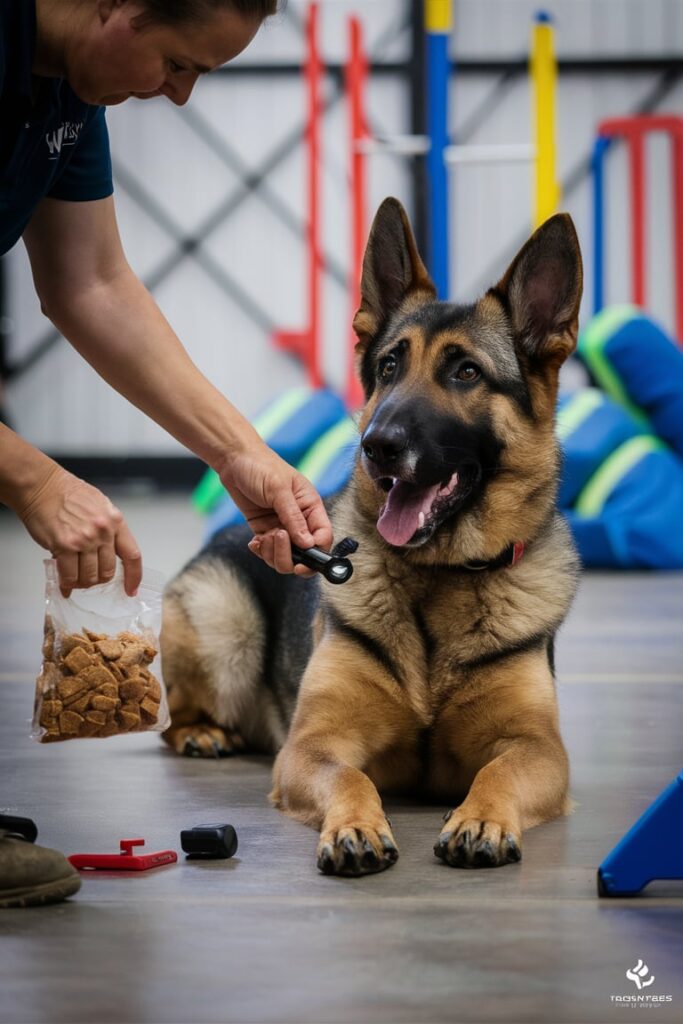

Training is crucial for ensuring that your guard dog performs effectively and safely. A well-trained guard dog will be both a loyal companion and a formidable protector. Here’s a comprehensive guide to training your guard dog, tailored to the specific needs of the best guard dog breeds.
Basic Training Principles
1. Consistency is Key:
- Why It Matters: Consistent commands and routines help your dog understand what is expected of them. Inconsistency can lead to confusion and behavioral issues.
- Implementation: Use the same commands and rewards for specific actions. Make training sessions regular and predictable.
2. Positive Reinforcement:
- Importance: Positive reinforcement encourages desired behaviors through rewards such as treats, praise, or playtime.
- How to Apply: Reward your dog immediately after they perform the desired action. This helps them associate the behavior with a positive outcome.
3. Clear Communication:
- Effective Commands: Use clear and distinct commands for different actions. Avoid using similar-sounding commands for different behaviors.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Incorporate hand signals or body language to reinforce verbal commands.
Advanced Training Techniques
1. Obedience Training:
- Commands to Master: Basic commands such as sit, stay, come, and heel are foundational. Advanced commands may include guard, alert, and release.
- Training Methods: Utilize clicker training, which involves using a clicker to mark correct behaviors followed by a reward.
2. Protection Training:
- Introduction to Protection: Begin with basic protection training, such as teaching your dog to bark on command and to stop barking on command.
- Controlled Aggression: Train your dog to show controlled aggression. This involves teaching them to assess a situation and react appropriately without unnecessary aggression.
- Professional Help: Consider hiring a professional trainer experienced in protection training, especially for high-drive breeds.
3. Socialization:
- Importance of Socialization: Proper socialization helps your guard dog distinguish between normal and threatening situations. It also prevents fear-based aggression.
- Exposure: Expose your dog to various people, animals, and environments. Ensure positive experiences to build confidence and adaptability.
Handling Behavioral Issues
1. Addressing Aggression:
- Identify Triggers: Understand what triggers aggressive behavior in your dog. It could be fear, lack of socialization, or territorial instincts.
- Professional Assessment: Consult with a behaviorist or trainer to address and manage aggression effectively.
2. Managing Fear:
- Desensitization: Gradually expose your dog to fear-inducing stimuli in a controlled manner. Pair these experiences with positive rewards to reduce fear.
- Confidence Building: Engage in activities that boost your dog’s confidence, such as agility training or positive reinforcement exercises.
3. Maintaining Focus:
- Distraction Training: Teach your dog to remain focused on commands even in distracting environments. Use high-value rewards to maintain their attention.
- Regular Training Sessions: Keep training sessions short but frequent to ensure your dog stays engaged and responsive.
Tips for Effective Training
1. Start Early:
- Puppy Training: Begin training your guard dog as early as possible. Early training helps shape their behavior and response to commands.
- Socialization Window: The critical socialization window is typically between 3 to 14 weeks of age. Maximize this period for optimal results.
2. Be Patient:
- Training Takes Time: Understand that training is a gradual process. Patience and persistence are key to achieving successful outcomes.
- Adjust Expectations: Set realistic goals and be prepared for setbacks. Consistent effort will lead to improvement over time.
3. Ensure Safety:
- Controlled Environment: Train in a controlled environment to ensure safety for both the dog and the trainer.
- Proper Equipment: Use appropriate training equipment, such as harnesses and muzzles, to manage your dog’s behavior safely.
Choosing the Right Guard Dog for Your Needs
Selecting the best guard dog breed for your specific needs involves evaluating several factors to ensure compatibility with your lifestyle, security requirements, and family dynamics. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you choose the right guard dog.
Assessing Your Needs
1. Security Requirements:
- Type of Protection Needed: Determine whether you need a dog primarily for home security, personal protection, or both. Different breeds offer varying levels of protection.
- Threat Level: Consider the type of threats you are likely to encounter and choose a breed known for effectively handling those situations.
2. Living Situation:
- Space Availability: Evaluate the space available in your home. Larger breeds typically require more room to move comfortably.
- Indoor vs. Outdoor: Decide whether the dog will primarily live indoors, outdoors, or both. Some breeds are more adaptable to indoor living, while others thrive in outdoor environments.
3. Family Dynamics:
- Children and Other Pets: Assess how the dog will interact with children and other pets in your household. Some breeds are better suited for families with children, while others may need careful socialization.
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Consider any allergies or sensitivities among family members that may affect your choice of breed.
Evaluating Different Breeds
1. Research Breeds:
- Breed Characteristics: Research the characteristics, temperament, and needs of various guard dog breeds. Use reliable sources and consult with breed experts or experienced owners.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Look for reviews and testimonials from current owners to gain insights into the breed’s behavior and suitability for different situations.
2. Meet Potential Breeds:
- Visit Breeders and Shelters: Visit breeders, shelters, or rescue organizations to meet potential guard dogs. Interact with the dogs to assess their temperament and behavior.
- Ask Questions: Inquire about the dog’s history, health, and training. Ask about any specific behaviors or issues that may affect their suitability as a guard dog.
3. Consider Training and Support:
- Training Requirements: Evaluate the training needs of the breed and ensure you have the time and resources to meet those needs. Some breeds require more intensive training and socialization.
- Support Resources: Seek out training resources, such as professional trainers, books, or online courses, to assist with training and behavior management.
Financial and Time Commitment
1. Costs:
- Initial Costs: Consider the cost of purchasing or adopting the dog, including any fees or expenses related to their acquisition.
- Ongoing Costs: Factor in ongoing expenses such as food, veterinary care, grooming, and training. Ensure you are prepared for the financial commitment.
2. Time Investment:
- Daily Care: Assess the time required for daily care, including feeding, exercise, grooming, and training.
- Long-Term Commitment: Recognize that owning a guard dog is a long-term commitment that requires consistent care and attention throughout their life.
Making the Final Decision
1. Reflect on Compatibility:
- Match Needs and Preferences: Reflect on how well the breed matches your security needs, living situation, and family dynamics.
- Assess Readiness: Ensure you are ready to meet the dog’s needs and provide the necessary care, training, and support.
2. Final Preparations:
- Prepare Your Home: Make any necessary adjustments to your home to accommodate the new dog, including securing outdoor areas and setting up a comfortable living space.
- Gather Supplies: Purchase essential supplies such as food, grooming tools, bedding, and training equipment.
3. Adoption or Purchase:
- Adoption: Consider adopting from a shelter or rescue organization, where you may find a suitable guard dog in need of a home.
- Purchase: If purchasing from a breeder, ensure they are reputable and provide a healthy, well-socialized dog.
FAQs

1. What are the best guard dog breeds for home security?
Some of the best guard dog breeds for home security include:
- German Shepherd: Known for their intelligence, loyalty, and protective instincts.
- Rottweiler: Recognized for their strength and assertiveness, making them excellent deterrents.
- Doberman Pinscher: Agile and alert, Dobermans are highly effective in guarding and protection.
- Bullmastiff: With their size and natural guarding tendencies, Bullmastiffs are great for protecting large properties.
2. How can I train my guard dog to be effective?
Training a guard dog involves:
- Consistency: Use the same commands and routines to avoid confusion.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward desired behaviors to encourage compliance.
- Obedience and Protection Training: Teach basic commands and advanced protection techniques, possibly with professional help.
- Socialization: Expose your dog to different environments, people, and animals to prevent fear-based aggression.
3. How do I choose the right guard dog breed for my family?
Consider these factors:
- Security Needs: Identify the type of protection you require.
- Living Situation: Assess the space available and whether the dog will be indoor or outdoor.
- Family Dynamics: Evaluate how the breed will interact with children and other pets.
- Training Commitment: Ensure you have the time and resources for the breed’s training needs.
4. What are the common health issues for guard dog breeds?
Common health issues can vary by breed but may include:
- German Shepherds: Hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and certain genetic disorders.
- Rottweilers: Hip and elbow dysplasia, heart problems, and certain cancers.
- Doberman Pinschers: Dilated cardiomyopathy, hip dysplasia, and von Willebrand’s disease.
- Bullmastiffs: Hip dysplasia, obesity, and certain types of cancer.
Regular veterinary check-ups and proper care can help manage these issues.
5. How much exercise does a guard dog need?
Guard dogs typically require:
- Daily Exercise: Most breeds need at least 30-60 minutes of exercise daily, including walks, playtime, and training sessions.
- Mental Stimulation: Engage them with interactive toys and training exercises to keep their minds sharp.
6. How can I manage a guard dog’s aggressive behavior?
To manage aggressive behavior:
- Identify Triggers: Determine what causes the aggression and address it.
- Professional Help: Consult a behaviorist or professional trainer for guidance.
- Controlled Exposure: Gradually expose your dog to stressors in a controlled environment while using positive reinforcement.
7. What should I include in my guard dog’s care routine?
A comprehensive care routine includes:
- Regular Veterinary Visits: For health check-ups and vaccinations.
- Proper Nutrition: A balanced diet suited to their breed and activity level.
- Grooming: Regular brushing, nail trimming, and ear cleaning.
- Training and Socialization: Ongoing training and exposure to various environments and situations.
8. How do I prepare my home for a guard dog?
Prepare your home by:
- Securing the Yard: Ensure fencing and outdoor areas are secure.
- Creating a Safe Space: Set up a comfortable area where your dog can retreat and relax.
- Gathering Supplies: Purchase essentials like food, grooming tools, and training equipment.
9. Should I adopt or buy a guard dog?
Both options have benefits:
- Adoption: Provides a home to a dog in need. Check local shelters or rescue organizations for suitable candidates.
- Buying: Allows you to select a specific breed with known characteristics. Ensure the breeder is reputable and ethical.
10. What are the long-term commitments of owning a guard dog?
Owning a guard dog involves:
- Daily Care: Regular feeding, exercise, grooming, and training.
- Financial Costs: Ongoing expenses for food, veterinary care, and supplies.
- Time Commitment: A significant investment of time for training, socialization, and interaction.
